Agmatinase Inhibition for Enhanced Neuroprotection
Introduction
This advanced technology focuses on the inhibition of mammalian agmatinase, offering a groundbreaking opportunity to explore new treatments for neurodegenerative diseases, brain injury, and mental health disorders. By inhibiting agmatinase, a key enzyme involved in polyamine metabolism, this technology regulates pathways critical to brain health and cellular protection. For pharmaceutical companies and biotech firms, this discovery opens the door to new therapies that can mitigate damage from neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and other brain-related disorders.
The Challenge: Preventing and Treating Neurodegenerative Damage
Neurodegenerative diseases and brain injuries are among the most complex and challenging conditions to treat. Current therapies focus mainly on symptom management, rather than addressing the root cause of neurodegeneration. This limits the ability of patients to experience meaningful long-term improvement. Additionally, inflammation and oxidative stress in the brain often lead to progressive damage, worsening conditions over time. There is an urgent need for therapeutic interventions that can target the molecular pathways involved in neuronal injury and degeneration.
Agmatinase Inhibition for Enhanced Neuroprotection
This technology addresses these challenges by targeting agmatinase, an enzyme that breaks down agmatine—a compound known for its neuroprotective effects. Inhibiting agmatinase can enhance agmatine levels, providing protection against oxidative stress, inflammation, and cell death. This method offers a potential therapeutic avenue for preventing neuronal damage, slowing disease progression, and improving cognitive function in patients with neurodegenerative conditions. The technology is versatile, with potential applications in treating traumatic brain injuries, stroke, and mental health conditions linked to brain chemistry imbalances.
Key Benefits for Pharmaceutical and Biotech Companies
For pharmaceutical developers, this agmatinase inhibition technology offers an exciting opportunity to create new neuroprotective drugs that address critical gaps in current treatments. By leveraging this mechanism, companies can develop treatments that not only reduce symptoms but also promote neuronal survival and function. Biotech firms can use this technology to explore broader therapeutic areas, such as improving recovery from brain injuries or enhancing cognitive resilience. Medical researchers and neuroscientists can further explore the molecular mechanisms of agmatine and its potential for treating mental health conditions like depression and anxiety.
Invest in Breakthrough Brain Health Solutions
Licensing this agmatinase inhibition technology gives your company access to cutting-edge solutions in neuroprotection and mental health treatment. With the growing demand for more effective therapies in the neurodegenerative and mental health space, this technology provides a pathway for developing innovative treatments that offer real hope for patients. It is a valuable investment for companies committed to advancing brain health and improving the quality of life for individuals affected by neurological disorders.
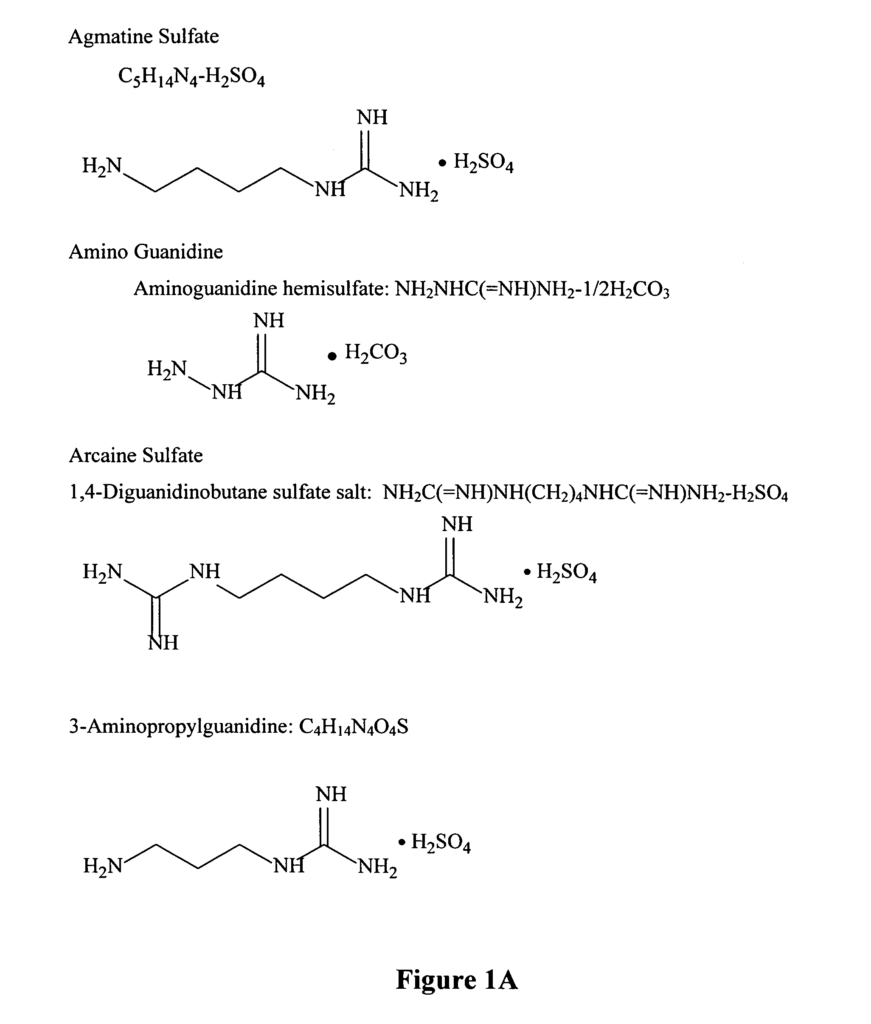
- Abstract
- Claims
Share
Title
Mammalian agmatinase inhibitory substance
Inventor(s)
John E. Piletz, Ming-Ju Huang, Kenneth S. Lee
Assignee(s)
Jackson State University
Patent #
7347984
Patent Date
March 25, 2008