Wonderful and Powerful CD19 CAR-T Therapy for Cancer Care
Introduction
This CD19-targeted CAR-T cell therapy provides a precise and potent approach to treating CD19-positive cancers, including various forms of lymphoma and leukemia. By using engineered CAR-T cells to specifically target and eliminate cancer cells expressing the CD19 antigen, this technology delivers focused immunotherapy, potentially improving survival rates and reducing side effects. For pharmaceutical and biotech companies in oncology, this CAR-T therapy is an invaluable asset, offering a pathway to develop cutting-edge cancer treatments that align with the growing demand for personalized, effective immunotherapies.
The Challenge: Enhancing Cancer Targeting with Precision
Traditional cancer treatments often struggle with achieving targeted action against cancer cells without impacting healthy tissues, leading to extensive side effects and reduced effectiveness. Patients with CD19-positive cancers face limited treatment options that precisely target cancerous cells, resulting in a need for therapies that combine high efficacy with patient safety. Given the complexities of cancer’s progression, healthcare providers need advanced treatments that address these challenges through innovative, personalized approaches, especially for patients in remission or those with aggressive disease variants.
CAR-T Cells for Precise Cancer Cell Elimination
This CD19-targeted CAR-T therapy technology enables healthcare providers to harness the body’s immune system to specifically target and destroy CD19-positive cancer cells. The therapy’s engineered CAR-T cells seek out and bind to CD19 antigens on cancerous cells, initiating a powerful immune response that eliminates malignancies without harming healthy tissues. Patients benefit from a more precise approach, with the therapy’s high specificity leading to fewer side effects, improved recovery, and enhanced quality of life. The technology’s adaptability to various CD19-positive cancers also broadens its therapeutic reach, supporting a wide range of oncological applications.
Key Benefits for Pharmaceuticals and Oncology Centers
For pharmaceutical developers, this CD19 CAR-T therapy provides a foundation to create a new generation of immunotherapies targeting hematologic cancers with unprecedented precision. Oncology centers can integrate this therapy to offer their patients an advanced, targeted treatment that improves outcomes and supports long-term recovery. This technology aligns with trends in personalized medicine, empowering healthcare providers to deliver patient-centered, tailored care. Its powerful, immune-mediated mechanism makes it a pivotal addition to cancer care, particularly for conditions where conventional therapies fall short.
Invest in the Future of Cancer Treatment
Licensing this CD19 CAR-T therapy technology positions your company at the forefront of immunotherapy and precision oncology. By offering a targeted, effective solution for CD19-positive cancers, your business can drive significant advancements in cancer care. This technology is a strategic investment for companies focused on improving patient outcomes, pioneering new immunotherapy options, and providing transformative cancer treatments that inspire hope and healing.
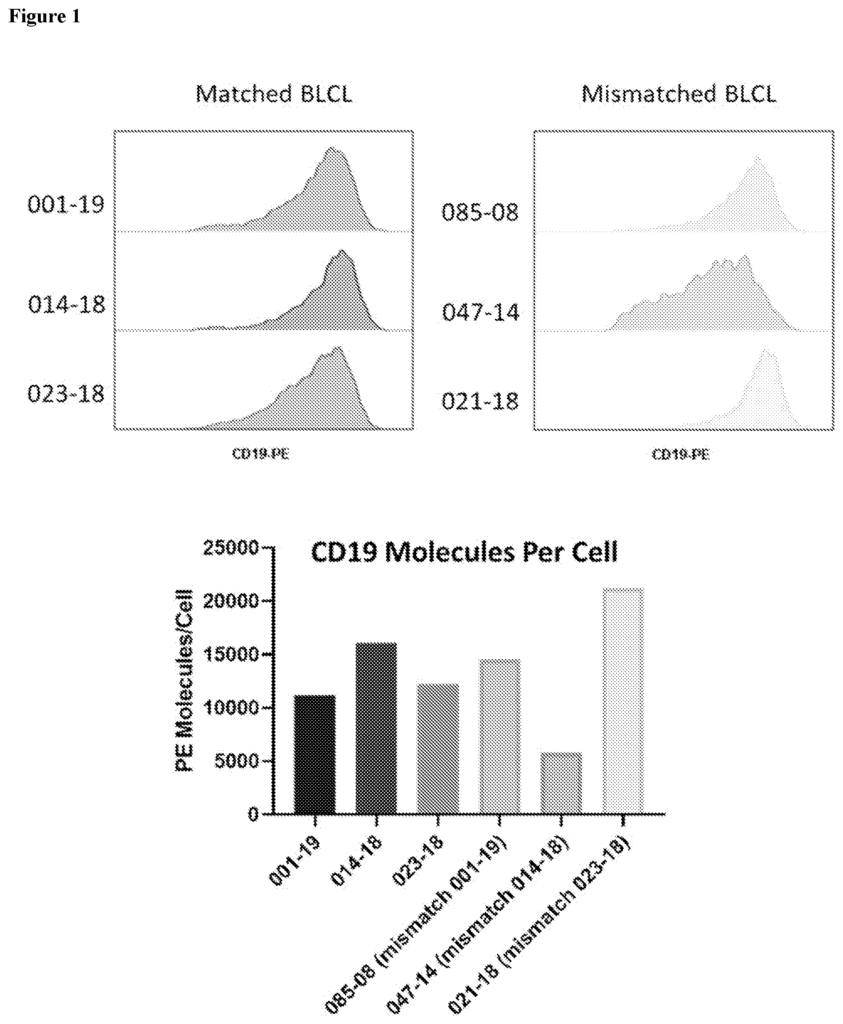
- Abstract
- Claims
Share
Title
Antigen specific cd19-targeted car-t cells
Inventor(s)
Blake T. Aftab
Assignee(s)
Atara Biotherapeutics Inc
Patent #
20220348649
Patent Date
November 3, 2022