Powerful Antiinfective Solutions for Tough Infections
Introduction
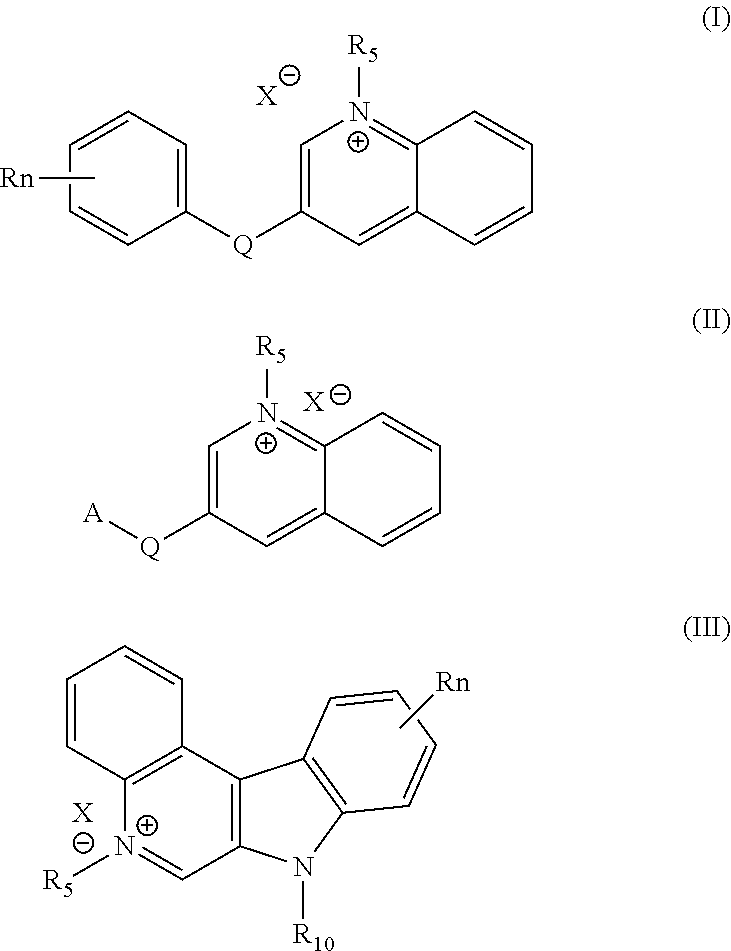
As infections become more resistant to current therapies, the healthcare and pharmaceutical industries face an urgent need for new, effective antiinfective agents. Drug-resistant pathogens pose a significant threat to global health, requiring innovative solutions to combat them. Our patented antiinfective compounds, based on 3-substituted quinolinium and 7H-indolo[2,3-c]quinolinium salts, provide a promising pathway to treat difficult infections. Whether you are a pharmaceutical company developing the next-generation antimicrobial drugs or a healthcare provider seeking effective treatments for resistant infections, these compounds offer a powerful, reliable option.
The Growing Threat of Antimicrobial Resistance
The rise of drug-resistant infections has become a global crisis. Bacteria and other pathogens are evolving to resist the effects of traditional antibiotics, leaving healthcare providers with fewer options to treat common and serious infections. As a result, infections that were once easily treated are becoming harder to control, leading to higher morbidity, mortality, and healthcare costs. The need for new antiinfective agents that can outpace resistance is greater than ever.
Pharmaceutical companies are challenged with developing therapies that can effectively target these resistant pathogens while minimizing side effects and improving patient outcomes. The demand for compounds that are both potent and adaptable to a wide range of infections is a growing priority for the industry.
Why Choose Powerful Antiinfective Solutions?
Our patented antiinfective compounds offer a potent, targeted approach to combating resistant pathogens. These quinolinium and indoloquinolinium salts are designed to disrupt the processes that allow pathogens to thrive, making them highly effective against a wide range of infections. Their unique chemical structure ensures that they can combat infections where traditional antibiotics have failed, providing a critical tool in the fight against drug-resistant microbes.
These compounds are versatile and can be developed into pharmaceutical products for both acute and chronic infections. They are ideal for addressing unmet needs in infectious disease treatment, offering new hope for patients who have limited treatment options.
Key Benefits
- Effective Against Resistant Pathogens: Targets drug-resistant bacteria and other microbes.
- Wide Application: Suitable for treating various types of infections.
- Potent and Reliable: Offers a powerful alternative to traditional antibiotics.
- Pharmaceutical Innovation: Supports the development of next-gen antimicrobial therapies.
Lead the Fight Against Infections with Powerful Antiinfective Solutions
Licensing these antiinfective compounds gives pharmaceutical companies the chance to address the growing crisis of antimicrobial resistance. These cutting-edge agents offer a unique, effective approach to treating infections that are resistant to existing drugs, providing a much-needed solution for healthcare providers and patients worldwide.
- Abstract
- Claims
or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, wherein:
Share
Title
3-substituted quinolinium and 7H-indolo[2,3-c]quinolinium salts as new antiinfectives
Inventor(s)
Seth Y. Ablordeppey
Assignee(s)
Florida Agricultural and Mechanical University FAMU
Patent #
8288410
Patent Date
October 16, 2012