Effortless Navigation for Complex Transit Hubs with Virtual Tile Routing
Introduction
As cities grow and public transportation systems become more complex, ensuring that passengers can easily navigate through sprawling transit hubs such as airports, train stations, and bus terminals becomes increasingly important. These locations, often designed with multiple levels, terminals, and interconnected routes, can overwhelm passengers, leading to missed connections, delays, and stress. Our patented virtual tile routing technology provides a seamless solution for enhancing the passenger experience by offering clear, personalized navigation assistance, making it easier than ever to move through complex transit hubs with confidence.
Current Frustrations in Transit Hub Navigation
For travelers, navigating a massive transit hub—especially during peak travel times or in unfamiliar locations—can be a daunting task. Complex layouts, multiple transit options, and limited signage often leave passengers feeling lost, which can result in missed departures, inefficiency, and unnecessary stress. Current navigation tools and apps often fail to provide real-time updates or detailed guidance through these intricate environments, leaving gaps in the user experience and creating barriers to efficient travel.
Transit operators and city planners are increasingly looking for innovative ways to optimize passenger flow, reduce congestion, and improve customer satisfaction. A navigation solution that offers clear, step-by-step guidance, with real-time data, is critical for ensuring passengers arrive at their destinations smoothly and on time.
A Cutting-Edge Solution for Seamless Transit Navigation
Our virtual tile routing technology provides an innovative approach to guiding passengers through complex transit hubs. This system creates a virtual map overlay of the hub, divided into tiles, allowing users to easily navigate even the most intricate layouts. Unlike static maps, this system provides real-time route adjustments and personalized directions based on a user’s location, offering a dynamic wayfinding experience that adapts to changes in the environment, such as gate changes, delays, or overcrowded areas.
This technology can be integrated into mobile apps and digital kiosks, providing passengers with an easy-to-use interface for precise navigation. From first-time travelers to frequent commuters, this tool significantly improves the overall transit experience, reducing stress and minimizing travel disruptions. It is particularly effective in hubs that are notorious for their size and complexity, such as international airports or large rail stations.
Key Benefits
- Real-Time Navigation: Provides continuously updated routes based on the user’s current location, accounting for changes in the environment.
- Personalized Directions: Offers step-by-step guidance tailored to each user’s transit needs, improving efficiency and reducing stress.
- Enhanced Passenger Experience: Simplifies navigation in large, complex hubs, leading to increased customer satisfaction.
- Broad Integration Potential: Can be integrated into existing mobile apps, digital kiosks, and transit management systems.
A New Standard in Passenger Wayfinding for Modern Transit Systems
Licensing this virtual tile routing technology offers transit authorities, city planners, and mobility solution providers a powerful tool for improving passenger movement through large, intricate transit hubs. By simplifying navigation and enhancing the travel experience, this system provides a key advantage in building more efficient, passenger-friendly transportation networks.
- Abstract
- Claims
What is claimed is:
1. A computer implemented system, comprising:
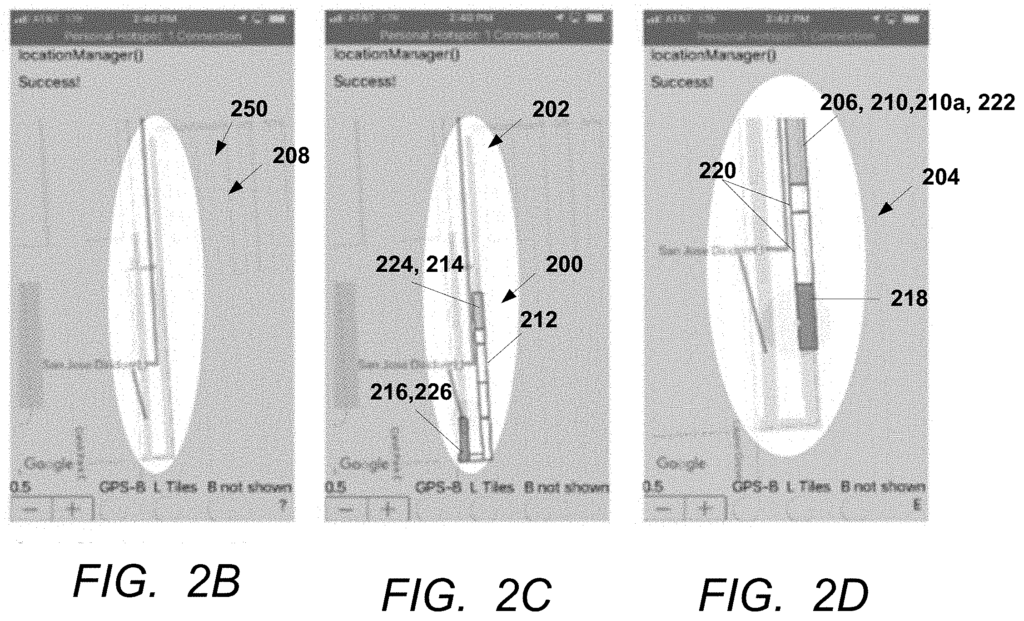
accesses a tessellated map, the tessellated map comprising a plurality of tiles on a map of a transit hub or plaza, wherein the tiles comprise:
causes a display or a speaker of a mobile device coupled to the one or more processors to:
3. The system of claim 1, wherein:
9. The system of claim 1, wherein the application causes the speaker of the mobile device to output:
12. The system of claim 1, wherein:
16. The system of claim 1, wherein:
17. A computer implemented method, comprising:
accessing a tessellated map, the tessellated map comprising tiles on a map of a transit hub or a plaza, wherein the tiles comprise:
Share
Title
Virtual tile routing for navigating complex transit hubs
Inventor(s)
Jonathan Lam, Fatemeh Mirzaei, Roberto Manduchi
Assignee(s)
University of California
Patent #
20210018321
Patent Date
January 21, 2021