Maximizing Efficiency with RFID-Enabled Component Tracking
Introduction
Managing and tracking components within devices is a challenge faced by many industries, from healthcare and aerospace to manufacturing and logistics. The ability to accurately monitor the use, lifespan, and condition of components can drastically reduce operational inefficiencies, increase product longevity, and prevent costly failures. This patented RFID-based tracking system provides an innovative solution to these challenges, offering an automated method to track the use of components embedded in devices—bringing precision and efficiency to industries that rely on managing high-value assets.
The Problem with Manual Tracking
Traditional methods of tracking components, such as manual logs or barcode scanning, are often time-consuming, error-prone, and difficult to scale. Human error, lost records, or missed inspections can lead to maintenance oversights, increased downtime, and costly equipment failures. In industries where precision and regular maintenance are critical, such as aerospace, healthcare, and high-value electronics, the stakes are even higher. Companies need an automated solution that provides real-time insights into component usage and conditions.
A Smarter, Automated Solution
This RFID-enabled tracking system is designed to automate the monitoring process by embedding RFID tags in components and devices. These tags store valuable data on component usage, enabling companies to track and monitor parts throughout their entire lifecycle. Whether it’s tracking how long a specific part has been in use, ensuring compliance with maintenance schedules, or managing warranty claims, this system offers a smart, hands-free solution to optimize operations.
With RFID’s real-time capabilities, companies can automate maintenance alerts and gain full visibility into their assets, ensuring that critical components are inspected or replaced at the right time. This level of transparency ensures compliance with regulatory standards while enhancing the reliability and performance of essential devices.
Key Advantages
- Reduced Operational Costs: Automating the tracking of components helps minimize labor costs, reduce downtime, and prevent equipment failures by ensuring timely maintenance.
- Increased Accuracy: RFID eliminates the risk of human error in tracking, ensuring more accurate data and reducing the likelihood of missed maintenance or replacements.
- Improved Asset Management: Gain real-time visibility into the lifespan and condition of high-value components, allowing for better planning and reduced unexpected costs.
- Scalable and Adaptable: Whether you are managing a large fleet of medical devices, aerospace components, or high-tech equipment, this system can easily scale to fit any industry’s needs.
A Step Toward Optimized Operations
Licensing this RFID-enabled component tracking system offers industries the chance to streamline operations, enhance equipment reliability, and reduce costs through automated tracking. It is a smart investment in the future of asset management, ensuring that components perform optimally while lowering the risk of costly equipment failures.
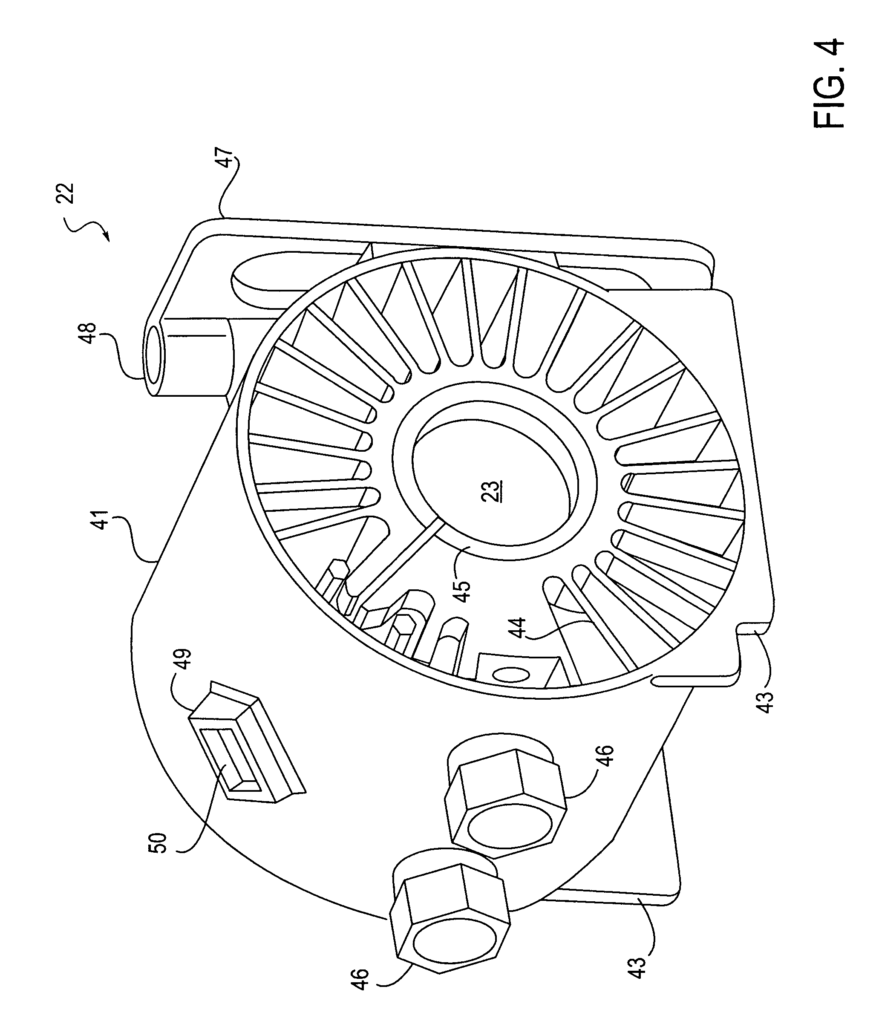
- Abstract
- Claims
1. A method of operating a device including a removable component, the method comprising the steps of:
6. A method of operating a device including a removable component, the method comprising the steps of:
Share
Title
Apparatus and method for using RFID to track use of a component within a device
Inventor(s)
Hasan Ertas, Brannon P. Wells, Rajeshwari Srinivasan
Assignee(s)
Stryker Corp
Patent #
7154378
Patent Date
December 26, 2006