Next-Gen Glucose Detection with Nanofiber Precision
Introduction
This cutting-edge carbon nanofiber sensor technology provides a non-enzymatic approach to glucose detection, offering a more accurate, reliable, and efficient method for monitoring blood sugar levels. Ideal for medical device companies, biotechnology firms, and diabetes management providers, this sensor technology enables more precise glucose readings without the need for enzymes, making it a robust solution for both consumer and clinical applications. It represents a breakthrough in glucose monitoring, addressing key industry challenges and offering enhanced performance for better patient outcomes.
The Challenge: Improving Glucose Detection Accuracy
Traditional glucose monitoring systems often rely on enzyme-based sensors, which can degrade over time, leading to inconsistent results and reduced accuracy. For individuals managing diabetes, the ability to trust glucose readings is crucial for proper disease management and quality of life. Additionally, enzyme-based sensors may be susceptible to interference from external factors, limiting their effectiveness. As the healthcare industry pushes toward more accurate, reliable, and long-lasting glucose detection methods, there is a growing need for non-enzymatic solutions that provide consistent performance without the drawbacks associated with enzymatic degradation.
Carbon Nanofiber Sensors: A Game-Changing Solution
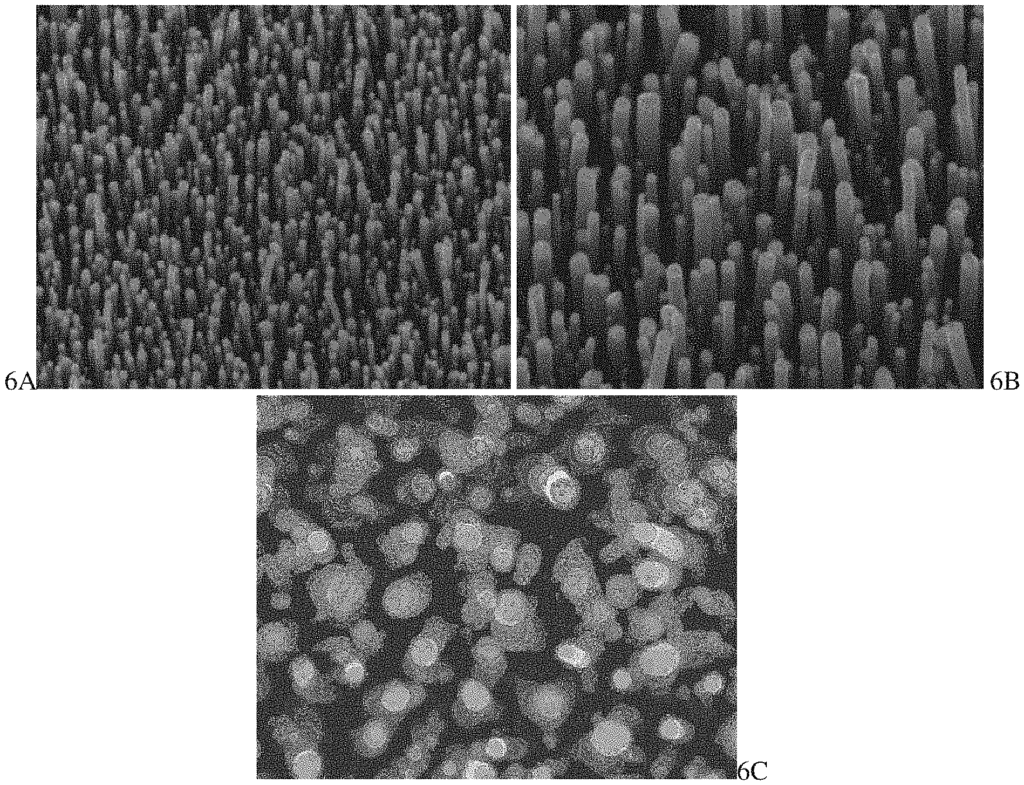
This carbon nanofiber sensor technology addresses these issues by using a non-enzymatic approach that leverages the high surface area and conductivity of carbon nanofibers to detect glucose levels with exceptional precision. The non-enzymatic method eliminates the risk of sensor degradation, offering longer-lasting accuracy and reducing the need for frequent recalibration. Additionally, the nanofiber structure enables faster, more reliable glucose detection, improving both patient experience and clinical outcomes. This technology is suitable for integration into wearable devices, continuous glucose monitors, and handheld meters, providing flexibility across a range of healthcare applications.
Key Benefits for Healthcare and Diagnostics
For medical device manufacturers, this technology enables the development of more reliable glucose monitoring systems that can enhance patient care and improve device longevity. Healthcare providers benefit from increased accuracy and fewer false readings, ensuring better patient management and treatment plans. Biotechnology firms can leverage this technology for further research into non-enzymatic detection methods, opening new avenues for diagnostic innovation. Diabetes management providers will find this technology valuable for improving patient compliance and health outcomes, offering a solution that reduces the burdens of frequent testing.
Investing in the Future of Glucose Monitoring
Licensing this nanofiber glucose detection technology positions your organization as a leader in the next generation of glucose monitoring. By offering a non-enzymatic solution that enhances precision and durability, your company can provide a more reliable tool for diabetes management, meeting the growing demand for accurate, easy-to-use monitoring systems. This technology supports better patient care, reduces costs associated with sensor maintenance, and advances healthcare innovation in glucose monitoring.
- Abstract
- Claims
The invention claimed is:
7. A method for detecting glucose in a sample, comprising:
Share
Title
Carbon nanofiber sensor for non-enzymatic glucose detection and methods of glucose detection using such carbon nanofiber sensor
Inventor(s)
Tamara Floyd SMITH, Julaunica TIGNER, Jessica KOEHNE
Assignee(s)
Tuskegee University
Patent #
11035820
Patent Date
June 15, 2021