Perfect Alignment: Precision Calibration for Augmented Reality Experiences
Introduction
The world of augmented reality (AR) has gained tremendous momentum, with applications spanning across industries such as gaming, entertainment, healthcare, and design. In these AR environments, the seamless integration of virtual objects into the real world is crucial for creating an immersive and realistic experience. However, one of the key challenges lies in accurately aligning virtual objects with their real-world counterparts, which can make or break the success of an AR experience. Our patented calibration techniques offer a solution to this issue, ensuring precise alignment between real and virtual objects in augmented reality environments.
Overcoming Alignment Issues in AR
In many current AR systems, inconsistencies in the alignment between real-world and virtual objects can lead to a disjointed or disrupted experience. For instance, in an AR training simulation, if a virtual tool doesn’t align perfectly with its real-world counterpart, the training experience loses its value and precision. The same holds true in industries like gaming and entertainment, where a misaligned virtual object can diminish the immersive experience that AR is designed to deliver.
Poor alignment not only hampers user satisfaction but can also result in inaccurate data interpretation, especially in fields like healthcare, where AR is being used for surgical simulations or patient diagnostics. Precise calibration is critical to providing the real-world accuracy that industries increasingly expect from AR solutions.
A Cutting-Edge Calibration Solution
Our patented calibration techniques are designed to address these alignment issues head-on, offering a powerful method to achieve real-time, precise calibration between virtual objects and their real-world counterparts. This technology enables AR systems to dynamically adjust and fine-tune the alignment, ensuring that virtual objects appear seamlessly integrated into the physical environment.
Whether it’s an AR app for furniture design, where virtual models need to fit perfectly into a real room, or a complex manufacturing process requiring real-time precision with virtual overlays, our calibration techniques ensure that the AR experience remains accurate and reliable.
What Makes This Technology Stand Out
- Unmatched Precision: Achieving pixel-perfect alignment between real and virtual objects enhances user satisfaction and improves the overall functionality of AR applications.
- Dynamic Calibration: Our techniques allow for real-time calibration, continuously adjusting and maintaining alignment as the user interacts with the environment.
- Versatile Applications: This technology is highly adaptable, making it applicable to various industries including gaming, manufacturing, healthcare, and education.
- Enhanced User Experience: Accurate calibration leads to more immersive and reliable AR experiences, whether for entertainment or professional use.
Why License This Technology
Licensing this patented calibration technique offers your company a cutting-edge tool to elevate AR experiences by addressing one of the most critical challenges in the field—alignment accuracy. With applications across multiple industries, this technology has the potential to enhance everything from AR gaming to industrial design, ensuring that virtual objects behave precisely as intended in the real world.
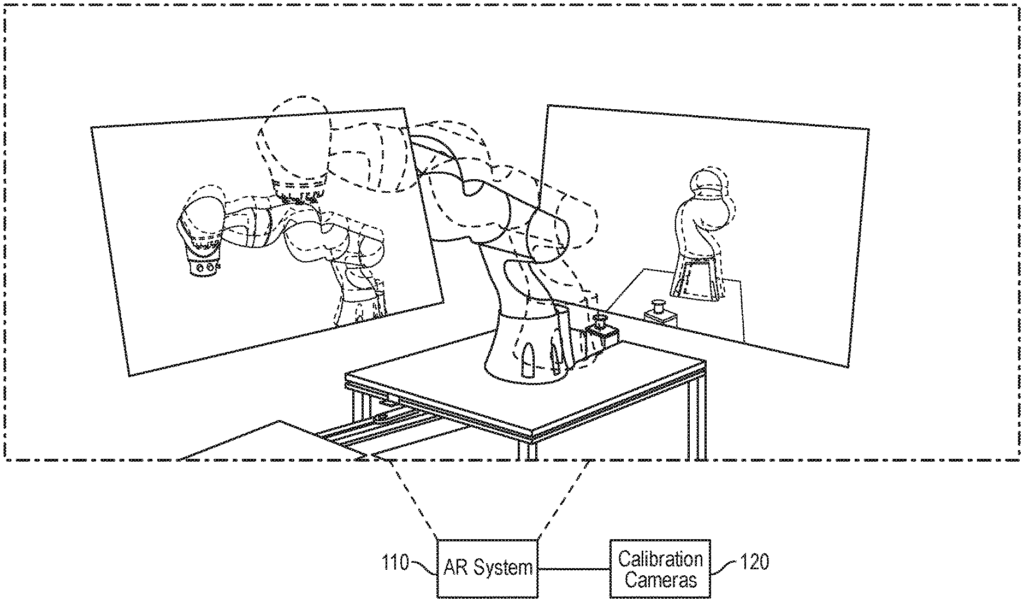
- Abstract
- Claims
What is claimed is:
Share
Title
Calibration techniques for aligning real-world objects to virtual objects in an augmented reality environment
Inventor(s)
Nassir Navab, Javad Fotouhi
Assignee(s)
Johns Hopkins University
Patent #
11367226
Patent Date
June 21, 2022