Shape the Future with Bendable Electronics: The Innovation You Can Feel
Introduction
Imagine a world where your electronics aren’t just tools—they’re extensions of your life, seamlessly bending, flexing, and adapting to every move you make. Welcome to the cutting edge of technology with our patented “Flexible Electrical Devices and Methods” (Patent #10386326).
The Problem
The rigidity of traditional electronics limits their potential. They’re stiff, unyielding, and confined to the flat and fixed. In a market hungry for innovation, the demand for electronics that can stretch, twist, and curve around our increasingly dynamic lives is at an all-time high.
The Breakthrough
This patent isn’t just about making devices that can flex; it’s about unleashing a new wave of possibilities. Think of wearables that wrap comfortably around your wrist, medical devices that contour perfectly to the body, or gadgets that fold and unfold like paper without a hitch. Our technology paves the way for a world where electronics are as fluid as your imagination.
Why This Matters
- Adaptability Redefined: Step into markets craving innovation—wearable tech, foldable phones, and beyond—with devices that break free from the constraints of rigidity.
- Design Beyond Boundaries: This technology empowers you to create products with shapes and functions never before possible, opening doors to truly groundbreaking designs.
- Future-Proof Your Portfolio: As industries pivot toward flexibility, be the first to offer products that not only meet this demand but set the standard.
The Invitation
Don’t just keep up with the future—shape it. License our flexible electrical devices technology and bring your boldest visions to life.
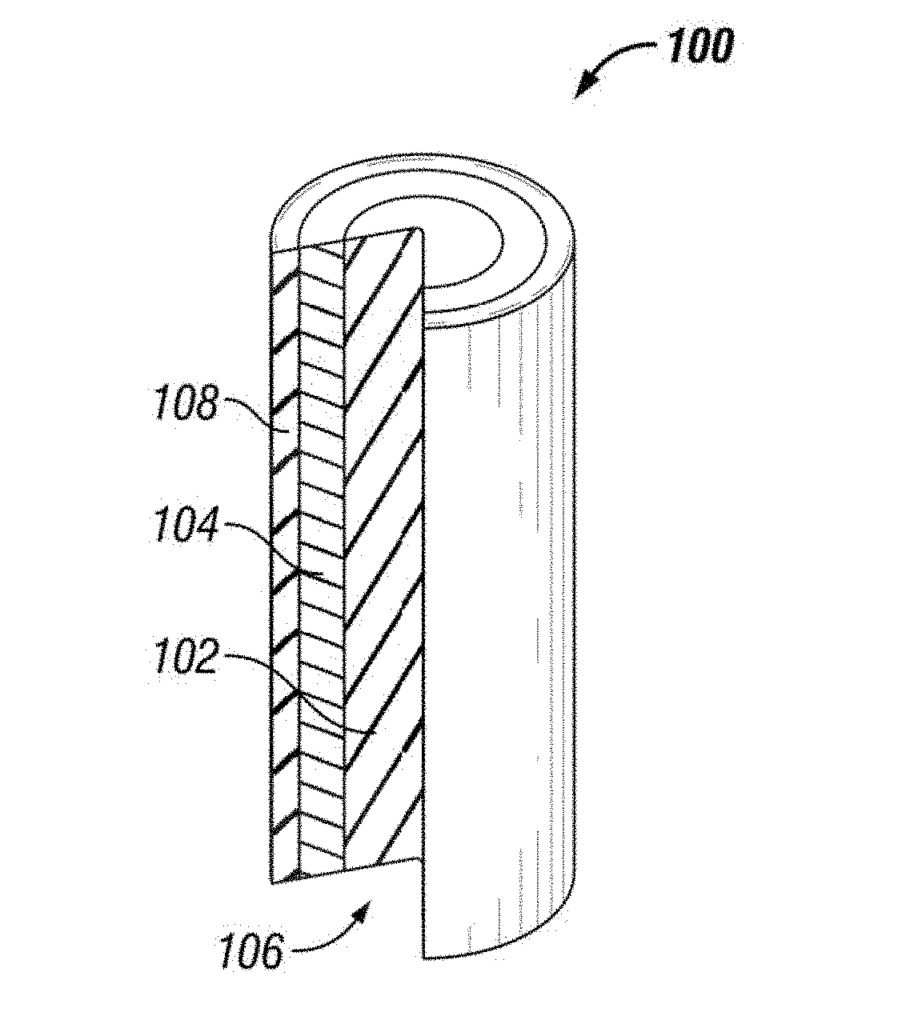
- Abstract
- Claims
We claim:
1. A method for fabricating an electrical component, the method comprising:
10. The method of claim 1, further comprising:
Share
Title
Flexible electrical devices and methods
Inventor(s)
Jesse Smithyman, Zhiyong Liang
Assignee(s)
Florida State University Research Foundation Inc
Patent #
10386326
Patent Date
August 20, 2019