Targeting Kynurenine Pathway for Innovative Therapeutic Applications
Introduction
The kynurenine pathway plays a pivotal role in several biological processes, including immune regulation, inflammation, and neurotransmitter balance. Dysregulation of this pathway has been linked to numerous diseases, from cancer and autoimmune disorders to neurodegenerative and psychiatric conditions. Our patented human kynureninase enzyme technology offers a unique approach to modulating this key metabolic pathway, providing new opportunities for treating conditions that have historically been challenging to manage with traditional therapies.
The Growing Importance of Metabolic Pathways in Disease
In recent years, there has been increasing recognition of the kynurenine pathway’s role in disease progression, particularly in immune regulation and inflammation. Elevated levels of kynurenine are associated with immune suppression, allowing cancer cells to evade immune detection, while disruptions in tryptophan metabolism through this pathway have been implicated in neurodegenerative diseases, psychiatric disorders, and inflammatory conditions.
Traditional treatments often fail to address the root causes of these conditions, focusing instead on symptom management. However, therapies that modulate the kynurenine pathway represent a promising new frontier for more targeted interventions that can address the underlying biochemical imbalances contributing to disease.
The Potential of Kynureninase Enzyme Therapy
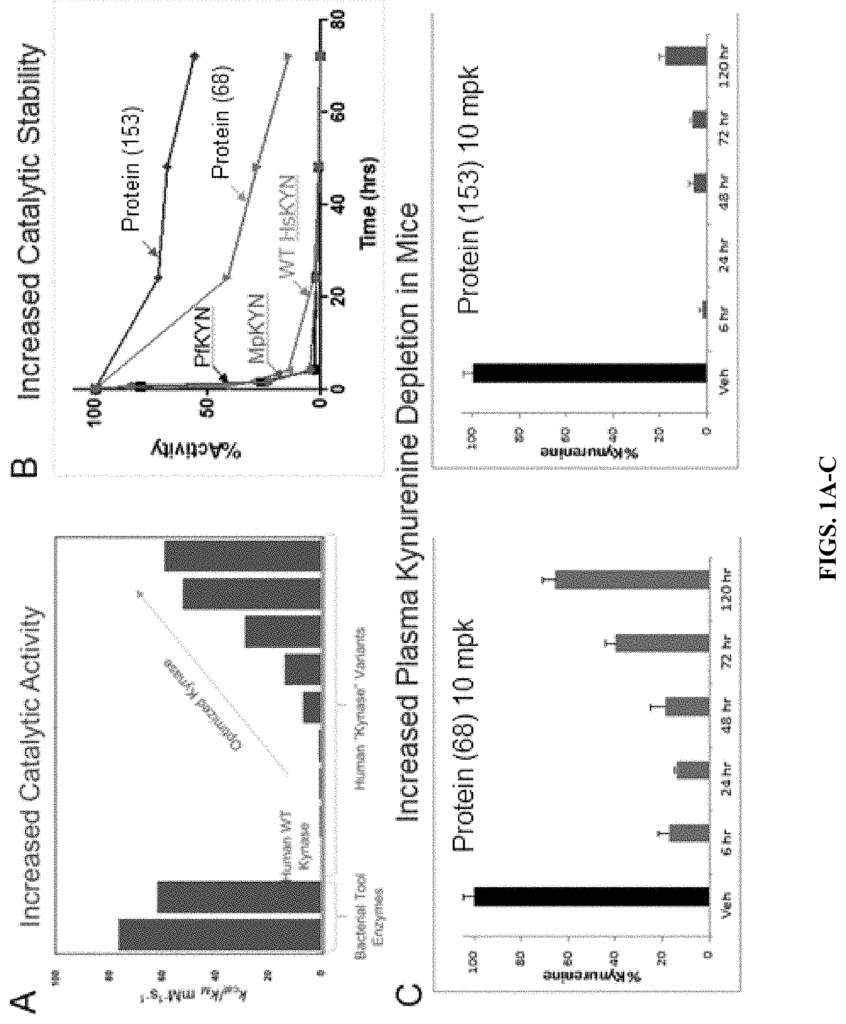
Our human kynureninase enzyme technology offers a targeted approach to modulating the kynurenine pathway. By degrading kynurenine, this enzyme can help restore balance in tryptophan metabolism, reducing the immunosuppressive effects associated with elevated kynurenine levels. This has significant implications for cancer immunotherapy, where tumor cells exploit this pathway to escape immune surveillance. By depleting kynurenine, this enzyme has the potential to enhance immune system response and improve the efficacy of existing cancer treatments, such as checkpoint inhibitors.
Beyond oncology, kynureninase enzymes could be applied to treat a range of diseases where the kynurenine pathway is implicated, such as neurodegenerative conditions (e.g., Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s disease), psychiatric disorders, and autoimmune diseases. This enzyme-based approach provides a more precise way to regulate metabolic imbalances that are difficult to address through traditional pharmacological interventions.
Key Benefits
- Targeted Immune Modulation: Reduces immunosuppressive kynurenine levels, potentially improving cancer treatment outcomes.
- Versatile Applications: Applicable to a broad range of diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and autoimmune conditions.
- Synergistic with Existing Therapies: Can be combined with cancer immunotherapies or treatments for neurodegenerative conditions to enhance efficacy.
- Minimized Side Effects: Focuses on modulating specific metabolic pathways, reducing the likelihood of off-target effects.
A New Era in Disease Treatment
Licensing this human kynureninase enzyme technology offers an opportunity for pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies to lead in developing advanced therapies targeting the kynurenine pathway. By addressing the root causes of immune dysregulation and metabolic imbalances, this technology represents a significant step forward in treating cancer, neurological diseases, and immune disorders.
- Abstract
- Claims
What is claimed is:
Share
Title
Human kynureninase enzymes and uses thereof
Inventor(s)
George GeorgiouEverett StoneJohn BlazeckChristos KARAMITROS
Assignee(s)
University of Texas System
Patent #
11648272
Patent Date
May 16, 2023