Simplify Optoelectronic Innovation with Single-Layer Pero-PEO LEDs
Introduction
Organometal halide perovskite (Pero) materials have been recently intensively explored. They are ideal in forming optoelectronic devices due to their optical and electronic properties. For example, solar cells with a thin layer of methyl ammonium lead iodide have achieved about 20% power conversion efficiency, approaching the state-of-the-art performance of polycrystalline thin film solar cells. Pero materials also exhibit high photoluminescence yield and can be tuned to cover the visible spectrum, thus they are potentially valuable in light-emitting diodes (LEDs) for information displays and lighting luminaires.
We have created single-layer LEDs using a composite thin film of Pero and poly(ethylene oxide) (PEO). In contrast to the multi-layer strategy, a simplified device structure is certainly advantageous in terms of processing flexibility and fabrication cost at the manufacturing stage. Our single-layer thin films are synthesized by a one-step spin coating process and have a device structure that resembles “bottom electrode (ITO)/Pero-PEO/top electrode (In/Ga or Au)”. In spite of the simple device structure, the green emission LEDs with methylammonium lead bromide (bromide-Pero) and PEO composite thin films exhibit a low turn-on voltage of ~2.8-3.1V (defined at 1 cd m-2 luminance), a maximum luminance of 4064 cd m-2 and a moderate maximum current efficiency of ~0.24-0.74 cd A-1. Such performance is on par with reported results in literature involving a more complex multi-layer device structure. Blue and red emissions LEDs have also been fabricated.
- Abstract
- Claims
Single – layer LEDs were developed using a composite thin film of organometal halide perovskite ( Pero ) and poly ( ethylene oxide ) ( PEO ) . Single – layer Pero LEDs have a device structure that resembles “ bottom electrode ( ITO ) / Pero – PEO / top electrode ( In / Ga or Au ) ” . Green emission LEDs with methylammonium lead bromide ( bromide – Pero ) and PEO composite thin films exhibit a low turn – on voltage of about 2 . 8 – 3 . 1 V ( defined at 1 cd m – 2 luminance ) , a maximum luminance of 4064 cd m – 2 and a moderate maximum current efficiency of about 0 . 24 – 0 . 74 cd A – 1 . Blue and red emission LEDs have also been fabricated using C1 / Br or Br / 1 alloyed Pero – PEO composite thin films .
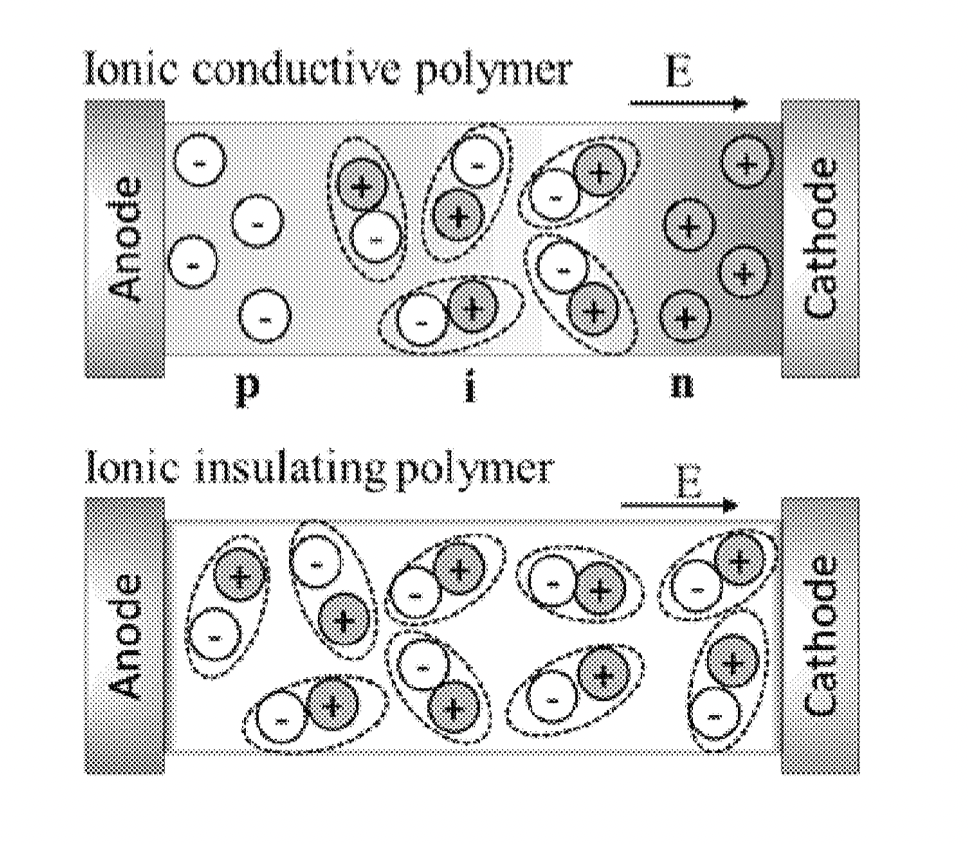
What is claimed is : 1 . A method for producing a single layer thin film opto electric device , comprising : forming an organometal halide perovskite ( Pero ) precursor ; adding an ionic – conducting polymer ( ICP ) to the Pero precursor to form a Pero – ICP precursor ; coating a substrate with the Pero – ICP precursor to form a Pero – ICP composite layer ; and annealing the Pero – ICP composite layer . 2 . The method of claim 1 , wherein the Pero precursor comprises a mixture of AX and BX , where A is a cation , B is a metal , and X is a halide ion . 3 . The method of claim 2 , wherein A comprises methyl ammonium ( CH3NH3 ) , formamidinium ( NH2CHNH2 ) , cesium ( Cs ) , or mixtures thereof . 4 . The method of claim 2 , wherein B comprises lead ( Pb ) , tin ( Sn ) , germanium ( Ge ) , or mixtures thereof . 5 . The method of claim 2 , wherein X comprises fluoride ( F ) , chloride ( C1 ) , bromide ( Br ) , iodide ( 1 % ) , astatide ( At ) , or mixtures thereof . 6 . The method of claim 2 , wherein forming the Pero precursor comprises mixing AX and BX in a ratio of approximately 1 . 5 mole AX to 1 mole BX . 7 . The method of claim 6 , wherein the Pero precursor further comprises dimethylformamide or dimethylsulfoxide . 8 . The method of claim 1 , wherein the ICP comprises oligomers or polymers of ethylene oxide , a polysaccharide polymer , or a conjugated polymer . 9 . The method of claim 1 , wherein the weight percent of the ICP relative to the weight of the Pero in the Pero – ICP precursor ranges from about 5 percent to about 75 percent . 10 . The method of claim 1 , wherein the Pero – ICP composite layer comprises methylammonium lead halide ( CH NH PbX ) , formamidinium lead halide ( NH CHNH , PbXz ) , cesium lead halide ( CsPbXz ) , or mixtures thereof , wherein X is a halide . 11 . The method of claim 1 , wherein coating the substrate comprises spin coating the organometal halide perovskite precursor onto the substrate . 12 . The method of claim 11 , wherein a duration of the spin coating step comprises approximately 60 seconds . 13 . The method of claim 1 , wherein annealing the Pero ICP composite layer comprises heating to approximately 60° C . for 3 minutes . 14 . A method for producing a single layer thin film optoelectric device , comprising : forming an organometal halide perovskite ( Pero ) precursor by dissolving methylammonium chloride ( CH3NH2Cl ) and lead chloride ( PbCl2 ) in a dimethyl sulfoxide , or by dissolving methylammonium bromide ( CH3NH2Br ) and lead bromide ( PbBr » ) in N , N – dimethylformamide , or by dissolving methylammonium iodide ( CH3NH2I ) and lead iodide ( Pblz ) in N , N dimethylformamide ; adding poly ( etheylene oxide ) polymer ( PEO ) to the Pero precursor to form a Pero – PEO precursor ; coating a substrate with the Pero – PEO precursor to form a layer of Pero – PEO composite on the substrate ; and annealing the Pero – PEO composite layer . 15 . The method of claim 14 , wherein the Pero precursor comprises a molar ratio of lead chloride to methylammonium chloride of approximately 1 : 1 . 5 , a molar ratio of lead bromide to methylammonium bromide of approximately 1 : 1 . 5 , or a molar ratio of lead iodide to methyammonium iodide of approximately 1 : 1 . 5 . 16 . The method of claim 14 , wherein the coating the substrate comprises spin coating the Pero – PEO precursor onto the substrate . 17 . A single layer thin film optoelectronic device , comprising : an anode ; a photoactive layer ; and a cathode ; wherein the photoactive layer comprises a methylammonium lead halide ( CH2NH3PbXz ) deposited from a mixture of methylammonium halide ( CH3NH2X ) and lead halide ( PbX , ) and ion – conducting polymer in a solution of dimethylformamide or dimethylsulfoxide , and thermally annealed . 18 . The device of claim 17 , wherein the ICP comprises poly ( ethylene oxide ) . 19 . The device of claim 17 , wherein a molar ratio of lead halide to methylammonium halide in the mixture is approximately 1 : 1 . 5 . 20 . The device of claim 17 , wherein X comprises fluoride ( F – ) , chloride ( Cl – ) , bromide ( Br – ) , iodide ( 1 ‘ ) , astatide ( At ) , or mixtures thereof .
Share
Title
SINGLE - LAYER LIGHT - EMITTING DIODES USING ORGANOMETALLIC HALIDE PEROVSKITE / IONIC - CONDUCTING POLYMER COMPOSITE
Inventor(s)
Zhibin Yu, Junqiang Li, Sri Ganesh Rohit Bade
Assignee(s)
Florida State University Research Foundation Inc
Publication #
20180102494
Publication Date
April 12, 2018