Transforming Cancer Treatment by Targeting Adenosine-Mediated Immunosuppression
Introduction
Adenosine and methylthioadenosine (MTA) are critical molecules involved in cellular processes, but in cancer, they play a different role—contributing to immune evasion by suppressing the body’s natural immune response against tumors. Tumors exploit these molecules to create a hostile environment that weakens the immune system, making it more difficult for therapies like immunotherapy to work effectively. Our patented enzyme-mediated depletion technology offers an innovative way to disrupt this protective barrier by depleting adenosine and/or methylthioadenosine, allowing the immune system to regain its ability to fight cancer cells and enhancing the efficacy of cancer treatments.
The Challenge of Immunosuppression in Cancer
Cancer immunotherapy has made significant advances in recent years, with treatments like checkpoint inhibitors and CAR-T therapies offering new hope for patients. However, a major obstacle remains: the immunosuppressive microenvironment created by tumors. Adenosine, in particular, accumulates in the tumor microenvironment and actively suppresses immune cells, such as T cells and natural killer (NK) cells, which are essential for combating cancer. This immunosuppression severely limits the effectiveness of existing therapies, creating an urgent need for methods to neutralize these barriers.
For pharmaceutical companies and researchers, the ability to modulate the tumor microenvironment to overcome adenosine-mediated immunosuppression is key to advancing cancer treatment and improving patient outcomes.
An Innovative Approach: Enzyme-Mediated Depletion
Our patented technology introduces an enzyme-based approach that targets and depletes adenosine and/or methylthioadenosine in the tumor microenvironment. By breaking down these immunosuppressive molecules, this method restores the immune system’s ability to recognize and attack cancer cells. It acts as a complement to existing immunotherapies, enhancing their potency and increasing the likelihood of a sustained immune response against the tumor.
This approach has broad potential, not just in oncology but in immune-related diseases where adenosine and MTA accumulation suppress immune function. It can be applied in combination with other therapies, such as immune checkpoint inhibitors or chemotherapy, to provide a more comprehensive treatment strategy.
Key Benefits
- Overcoming Tumor Immunosuppression: Depletes adenosine and MTA, reducing immunosuppressive barriers and enabling a more effective immune response.
- Enhanced Immunotherapy: Boosts the efficacy of existing immunotherapies, such as checkpoint inhibitors and CAR-T cells.
- Broad Applications: Useful in cancer treatment and other immune-related conditions where adenosine accumulation is a problem.
- Synergistic Potential: Can be combined with a variety of cancer treatments for more comprehensive, multi-targeted strategies.
A New Avenue for Cancer Immunotherapy
Licensing this enzyme-mediated depletion technology offers pharmaceutical companies the opportunity to pioneer a new class of treatments that target tumor immunosuppression. By restoring immune function in the tumor microenvironment, this technology paves the way for more effective cancer therapies and better outcomes for patients.
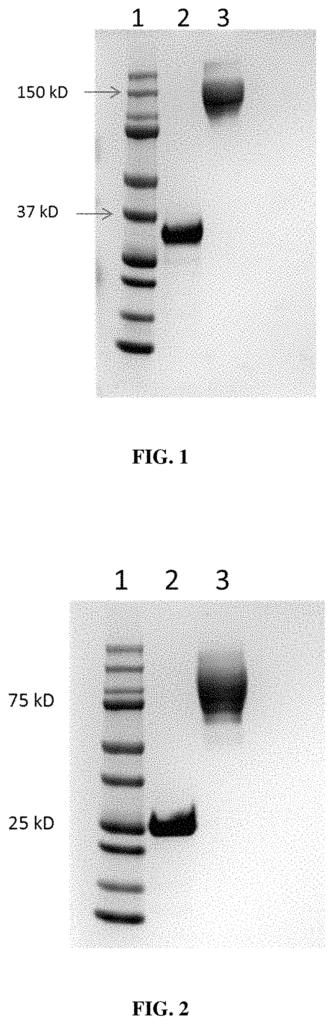
- Abstract
- Claims
What is claimed is:
1. A composition for treating a methylthioadenosine phosphorylase-deficient cancer comprising:
10. The method of claim 5, wherein the tumor comprises:
14. A method of treating a patient having a tumor comprising:
Share
Title
Enzyme-mediated depletion of adenosine and/or methylthioadenosine
Inventor(s)
Everett Stone, Donjeta GJUKA
Assignee(s)
University of Texas System
Patent #
11118167
Patent Date
July 14, 2021